Butterflies and moths are both insects belonging to the order Lepidoptera, but they have some key differences. Here are some of the most common ways to tell them apart:
Butterflies Vs. Moths:
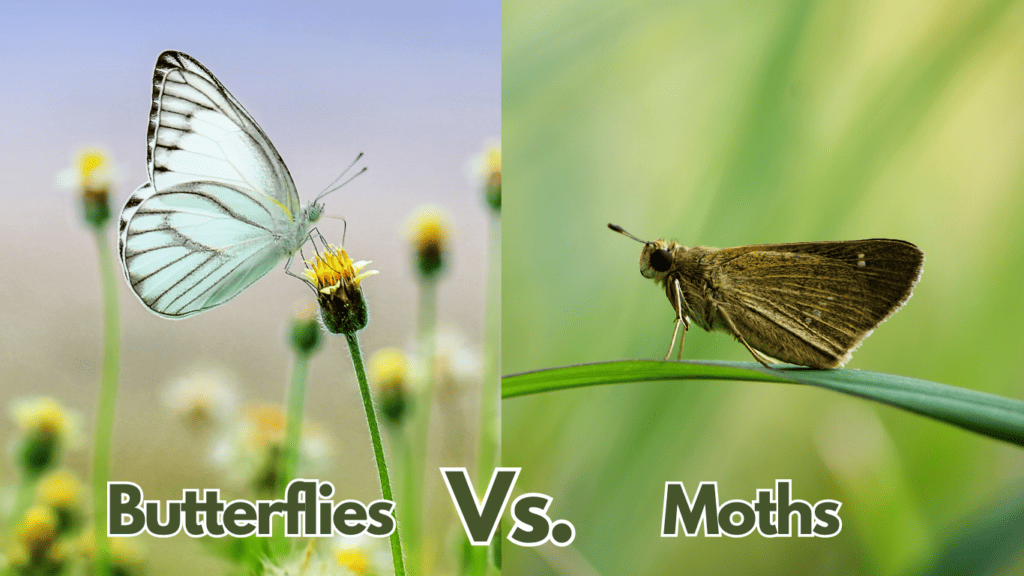
- Appearance: Butterflies are generally smooth and lean, while moths tend to be stockier and have furry bodies. Butterflies also have thin, straight, and long antennae with club-like tips, while moths have feathery, thick, comb-like antennae.
- Behavior: Butterflies are diurnal, meaning they are active during the day, while moths are nocturnal, meaning they are active at night. Butterflies usually rest with their wings held together behind their bodies, while moths fold their wings down over their bodies when resting.
- Life cycle: Butterflies usually make a chrysalis when they pupate, while moths make a cocoon.
It is important to note that there are exceptions to these differences, and some moths and butterflies can look very similar. However, these differences can be used as general guidelines to distinguish between the two.
Identification: Butterflies Vs. Moths
Physical Characteristics
One of the easiest ways to tell the difference between a butterfly and a moth is to look at their antennae. A butterfly’s antennae are club-shaped with a long shaft and a bulb at the end, while a moth’s antennae are feathery or saw-edged. Butterflies also have larger wings and a more slender body than moths. Additionally, butterflies tend to have brighter and more vibrant colors than moths, which often have more muted tones.
Behavioral Traits
Butterflies are typically active during the day and are attracted to brightly colored flowers, while moths are more active at night and are attracted to light sources. Butterflies also tend to fly in a more erratic and fluttery pattern, while moths have a more direct and steady flight.
Species Diversity
There are over 100 families of insects in the order Lepidoptera, which includes both butterflies and moths. While there is no real taxonomic difference between the two, some physical and behavioral characteristics can help differentiate them. Some species of moths are just as colorful as butterflies, so color alone is not a reliable indicator. However, certain species of butterflies, such as the swallowtail, can be identified by their clubbed antennae.
Anatomy and Physiology
Wing Structure
Both butterflies and moths have wings that are covered in scales, which give them their characteristic colors and patterns. However, there are some differences in the way their wings are structured. Butterflies tend to fold their wings vertically up over their backs, while moths tend to hold their wings in a tent-like fashion that hides the abdomen. Butterflies are typically larger and have more colorful patterns on their wings, while moths are typically smaller with drab-colored wings.
Antennae Types
One of the easiest ways to tell the difference between a butterfly and a moth is by looking at their antennae. Butterflies have thin antennae with a small ball or club at the end, while moth antennae can be quite varied in appearance and lack the club end. Some moths have feathery or comb-like antennae, while others have long, thin antennae that can be as long as their bodies.
Body Structure
The body structure of butterflies and moths is also different. Moths have a frenulum, which is a wing-coupling device that helps to keep their wings in place during flight. Butterflies, on the other hand, do not have a frenulum. In addition, moths tend to have a stockier body shape with a thicker abdomen, while butterflies have a more slender body shape with a thinner abdomen.
Life Cycle
From Larva to Adult
Both butterflies and moths go through a complete metamorphosis, which means they have four stages in their life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The larva stage is also known as the caterpillar stage. During this stage, the caterpillar eats and grows rapidly, shedding its skin several times until it reaches its full size. The larva then forms a cocoon or chrysalis.
Cocoon and Chrysalis
The cocoon and chrysalis are protective coverings that the larva creates before it transforms into an adult. Moths spin cocoons made of silk, while butterflies form chrysalises. Inside the cocoon or chrysalis, the caterpillar undergoes a remarkable transformation.
Metamorphosis Process
The metamorphosis process is a complex one. Inside the cocoon or chrysalis, the caterpillar’s body breaks down into a soup-like substance. From this soup, the adult butterfly or moth begins to form. The wings, legs, and other body parts develop, and the insect emerges from its cocoon or chrysalis as an adult.
During the adult stage, butterflies and moths mate and lay eggs, starting the life cycle all over again. The length of each stage in the life cycle can vary depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Behavioral Patterns
Day and Night Activities
One of the most significant behavioral differences between butterflies and moths is their activity patterns during the day and night. Butterflies are diurnal, which means they are active during the day. On the other hand, moths are nocturnal, which means they are active at night. This difference in activity patterns is due to their respective lifestyles and ecological niches.
Resting and Active Periods
Butterflies and moths also have different resting and active periods. Butterflies tend to rest with their wings folded vertically up over their backs, while moths tend to hold their wings in a tent-like fashion that hides the abdomen. Butterflies are typically more active during the day, while moths are more active at night. However, both butterflies and moths have periods of rest and activity throughout the day and night.
Activity Patterns
Butterflies and moths also have different activity patterns. Butterflies are typically larger and have more colorful patterns on their wings. They tend to fly in a straight line and are more active during the day. In contrast, moths are usually smaller and have more muted colors on their wings. They tend to fly in a zigzag pattern and are more active at night.
Adaptations and Survival Strategies
Camouflage and Mimicry
Butterflies and moths have evolved a variety of adaptations to help them survive in their environments. One of the most important of these adaptations is camouflage. Many species of butterflies and moths have evolved to blend in with their surroundings, making them difficult for predators to spot. Some species have developed patterns and colors that mimic the appearance of leaves or other objects in their environment.
In addition to camouflage, some butterflies and moths have evolved to mimic the appearance of other species. For example, some moths have evolved to look like wasps or bees, which can help them avoid being eaten by predators that are afraid of these insects.
Predator Evasion
Butterflies and moths also have a number of adaptations that help them evade predators. Some species are able to fly very quickly, making them difficult for predators to catch. Others have developed behaviors that make them difficult to find, such as hiding in crevices or under leaves during the day.
Caterpillars, the larval stage of butterflies and moths, also have a number of adaptations that help them avoid predators. Some species have spines or hairs that can be irritating or poisonous to predators. Others are able to produce a foul-smelling liquid that deters predators.
Resting Postures
When butterflies and moths are resting, they often adopt a specific posture that helps them avoid being seen by predators. Many species rest with their wings folded together, which can make them difficult to spot. Some species also rest with their wings spread out, which can help them absorb heat from the sun.
In addition to their resting postures, butterflies and moths have developed a variety of behaviors that help them avoid predators. For example, some species are able to detect the presence of predators and quickly fly away before they can be caught.
Ecology and Habitat
Feeding Habits
Both butterflies and moths feed on a variety of food sources, including flowers, nectar, and sap. Some species of moths are known to feed on rotting fruit, while others feed on animal carcasses. Butterflies, on the other hand, mainly feed on the nectar of flowers. They have long proboscises that allow them to reach deep into the flower to extract the nectar.
Migration Patterns
While some species of butterflies and moths migrate, not all do. The migration patterns of these insects vary depending on the species and their habitat preferences. Some species of butterflies, such as the monarch butterfly, migrate thousands of miles each year to reach their wintering grounds. Moths, on the other hand, tend to have more localized migration patterns, moving only short distances to find suitable habitats for feeding and reproduction.
Habitat Preferences
Butterflies and moths can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and even urban areas. However, their specific habitat preferences can vary greatly depending on the species. Some species of butterflies prefer open meadows with plenty of sunlight and flowers, while others prefer shady forests with damp soil. Moths, on the other hand, tend to prefer darker environments, such as forests and caves.
Unique Species
Monarch Butterfly
The Monarch Butterfly is one of the most well-known and recognizable butterfly species in the world. Their wings are a bright orange color with black veins and white spots. They are known for their long migrations, which can span thousands of miles across North America. Monarch Butterflies are also known for their unique life cycle, which includes four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
Luna Moth
The Luna Moth is a beautiful and unique moth species that is native to North America. They have a wingspan of up to 4.5 inches and are a pale green color with long, curving tails. Luna Moths are nocturnal and are attracted to light sources at night. They are also known for their short lifespan, which lasts only about one week.
Cabbage White
The Cabbage White is a common butterfly species that is found throughout Europe, Asia, and North America. They have white wings with black spots and are often seen fluttering around gardens and fields. Cabbage Whites are known for their ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats and their preference for feeding on plants in the mustard family.
Birdwings
The Birdwing Butterfly is a large and colorful butterfly species that is found in Southeast Asia and Australia. They have wingspans of up to 11 inches and are known for their bright colors and unique patterns. Birdwings are also known for their strong and fast flight, which allows them to travel long distances in search of food and mates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the physical differences between moths and butterflies?
One of the easiest ways to differentiate between moths and butterflies is by looking at their antennae. Butterflies have club-shaped antennae with a bulb at the end, while moths have feathery or saw-edged antennae. Additionally, butterflies tend to have more vibrant and colorful wings, while moths have more muted colors and often have fuzzy bodies.
What species of butterflies are yellow?
There are many species of butterflies that are yellow, including the Clouded Sulphur, the Tiger Swallowtail, and the Yellow Swallowtail. However, it’s important to note that not all yellow butterflies are the same species, and there can be variations in color and markings.
Are there any dangerous moths?
While most moths are harmless, there are a few species that can be dangerous. For example, the African armyworm moth has been known to cause significant crop damage, and the oak processionary moth can cause skin irritation and respiratory problems in humans.
What is the difference between moths and butterflies in the UK?
In the UK, moths and butterflies are both part of the Lepidoptera order of insects. However, moths tend to be more common and diverse in the UK, with over 2,500 species compared to around 60 species of butterflies. Additionally, moths are typically active at night, while butterflies are active during the day.
How can you tell if an insect is a moth or a butterfly?
Aside from looking at their antennae, there are a few other ways to distinguish between moths and butterflies. Moths tend to have thicker bodies and less colorful wings than butterflies. Additionally, moths often rest with their wings flat against their bodies, while butterflies tend to hold their wings upright.
What are the identifying features of moths?
In addition to their feathery or saw-edged antennae, moths often have fuzzy bodies and muted colors. Some species of moths also have distinctive markings on their wings, while others have wings that are plain or speckled. Additionally, some moths have unique features such as transparent wings or long tails.
Recent Posts
How Can I Create A Habitat For Skipper Butterflies In My Garden With 3 Easy Plants
Skipper butterflies are a diverse group of insects that are found all over the world. They are known for their quick, darting flight and their often colorful wings. Skippers are attracted to...
Common Species Of Butterflies In Maryland: 21 Unique Species
Maryland is home to a variety of beautiful butterflies, from the large and showy Eastern Tiger Swallowtail to the tiny and delicate Blue Dasher. There are over 150 species of butterflies in Maryland,...
